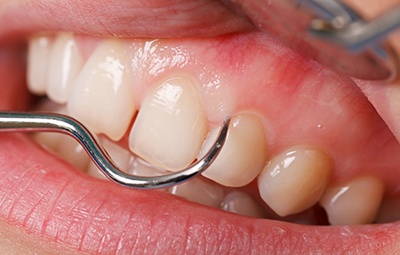
 Receding gums is where the gum tissue surrounding the teeth wears away or pulls back, exposing more of the tooth or tooth’s root surfaces. As well as leading to increased sensitivity and even pain, receding gums expose the root to bacteria and plaque. If left untreated, the gum tissue and bone structures of the teeth can be severely damaged and result in tooth loss.
Receding gums is where the gum tissue surrounding the teeth wears away or pulls back, exposing more of the tooth or tooth’s root surfaces. As well as leading to increased sensitivity and even pain, receding gums expose the root to bacteria and plaque. If left untreated, the gum tissue and bone structures of the teeth can be severely damaged and result in tooth loss.
Symptoms
Gum recession is a gradual condition that many people are unaware they have. Symptoms include:
- Bleeding after brushing or flossing
- Red, swollen gums
- Bad breath
- Sensitivity or pain at the gumline
- Noticeably shrinking gums, where a tooth might look “longer”
- Exposed tooth roots
- Loose teeth
Causes of Receding Gums
Receding gums can easily be diagnosed by your dentist. As they can be a sign of an underlying condition, it is important to see your dentist as soon as you notice any symptoms. Early detection and prevention are key.
Gum recession is most commonly caused by gum disease as a result of poor oral hygiene. Gum disease, which ranges in severity from gingivitis through to periodontal disease, is where plaque accumulates around the teeth and weakens the gums, causing them to recede. And even with great oral hygiene habits, some people can be more prone to gum disease because of inherited factors.
Brushing too hard and/or with a hard-bristled toothbrush can cause receding gums. This wears the enamel on your teeth away, and results in your gums receding.
Hormonal changes can make your gums more sensitive and susceptible to gum recession, particularly during puberty, pregnancy and menopause.
Smoking can leave a sticky plaque on your teeth which is difficult to remove and increases your risk of gum recession.
Grinding or clenching your teeth, known as bruxism, places undue force on the teeth and can lead to receding gums.
Treatment for Receding Gums
Gum disease can be stopped or even reversed if caught and treated early. Where gum disease is present, a rigorous oral hygiene regime is essential. As well as having meticulous brushing and flossing routines at home, regular dental hygiene appointments as recommended by your dentist or dental hygienist will provide in-depth cleaning, tooth scaling and root planing.
Where periodontal disease is advanced, treatment by a dentist specialising in periodontics may be required. This involves folding back affected gum tissue in order to remove harmful pockets of bacteria then resecuring the gum flap.
Desensitizing agents, varnishes and dentin bonding agents can all be used to effectively treat the sensitivity of exposed tooth roots. Composite or porcelain resins can be applied to fill gaps where gums have receded and cover the surface of the root.
It is possible to perform a gum graft to correct receding gums. In this procedure a periodontist will transplant tissue from the roof of your mouth or other healthy gum tissue to cover and protect the recession.
If you have concerns regarding receding gums, please contact us for an assessment. We can provide you with a range of treatment options specific to your needs.
